GAAP vs. IFRS: How Apple & Samsung Approach Financial Reporting
With GAAP keeping Apple’s financial reporting precise and stable, and IFRS offering Samsung the flexibility to thrive globally, these giants showcase the strategic impact of their chosen accounting frameworks.
📊 Here’s how the numbers stack up:
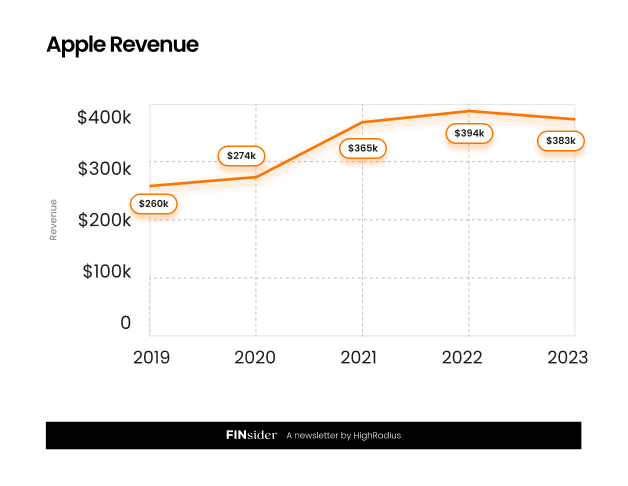
$383B Apple revenue reported under GAAP
$194B Samsung revenue reported under IFRS
20% Apple stock increase as per GAAP
10% Apple cost reduction as per GAAP
Yet, the core question remains: How do these frameworks shape each company’s financial transparency, investor confidence, and international reach?
Let’s dive deeper to understand how GAAP and IFRS uniquely influence Apple and Samsung! 🔍
How Do Apple’s GAAP and Samsung’s IFRS Reporting Standards Differ?
In 2023, Apple reported about $383B in revenues under GAAP, showcasing precision and stability that foster investor trust through reliable reporting. This contributed to strong profitability and effective asset management.
Conversely, Samsung reported around $194B, with IFRS allowing for more flexibility in accounting to reflect its diverse global operations.
Apple’s GAAP Reporting
GAAP, the U.S. rule-based framework, offers Apple a structured way to report its financial performance, as seen in its $383B revenue in 2023, demonstrating consistency and accuracy.
Revenue Recognition: Apple follows ASC 606, recognizing revenue only when obligations are met. For iPhones, revenue is recorded when the customer takes possession, typically at sale or shipment.
Net sales include revenue from iPhones, Macs, iPads, and Services, recognized upon control transfer. For instance, iPhone 15 revenue is recorded when shipping, while iCloud revenue is recognized over time.
Service Revenues: Apple recognizes revenue from services and subscriptions (e.g., iCloud, AppleCare) over the contract period, evenly distributing the revenue for a 12-month iCloud subscription throughout the year.
Samsung’s IFRS Reporting
In contrast, Samsung’s $194B revenue in 2023 was reported under IFRS, a flexible system that adapts to its diverse operations in hardware, semiconductors, and global services.
Revenue Timing Flexibility: Under IFRS 15, Samsung recognizes revenue based on performance obligations, allowing for progressive recognition from long-term semiconductor contracts as milestones are met.
Multiple Performance Obligations: Samsung bundles products and services, permitting distinct performance obligations for consumer electronics and service contracts. This IFRS flexibility enables tailored revenue recognition for different regions or sectors.
Can Apple’s GAAP Strategy Keep Investors Hooked?
Apple’s adherence to GAAP boosts investor confidence with transparent financial reporting. In 2023, its stock price rose 20%, reflecting trust in its performance.
GAAP's predictability reduces uncertainty and supports long-term confidence in financial health while minimizing legal risks and enhancing Apple’s domestic reputation.
Samsung's strong market position, with a 15% market capitalization growth in 2023, is bolstered by IFRS, which enhances transparency and boosts investor confidence.
💡 How does following GAAP rules help investors feel more secure about Apple? Know here.
Is Samsung’s IFRS Flexibility the Secret to Global Expansion?
Samsung's presence in over 80 countries is strengthened by IFRS, offering flexibility for international markets. Unlike Apple, which uses GAAP for the U.S., Samsung's use of IFRS has driven its global expansion.
In 2023, Samsung invested about $5B in foreign markets, demonstrating its adaptability to international regulations.
💡 How Has Samsung Benefited from IFRS in Global Operations? Know here.
Conclusion
Apple and Samsung show how GAAP and IFRS shape financial reporting and strategy. GAAP gives Apple stability and investor trust, while IFRS provides Samsung flexibility for global operations.
Each framework reflects their strategic priorities, highlighting their success in the global market.